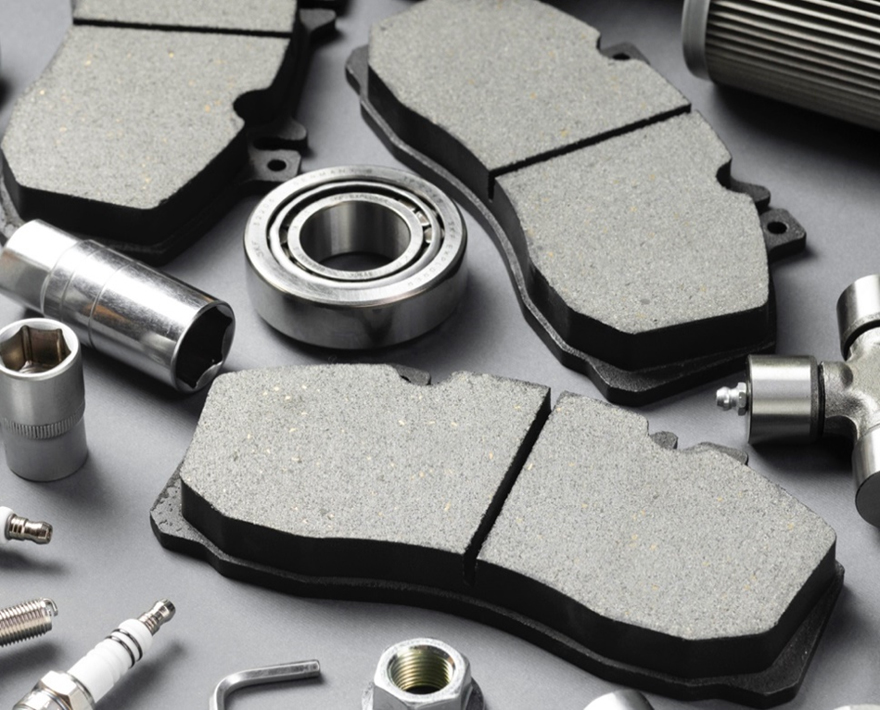
Brake pads are essential components of any vehicle's braking system, providing the crucial friction needed to slow down or stop a moving vehicle safely. Here's everything you need to know about Disc brake pads:
What Are Brake Pads?
Brake pads generally consist of a metal backing plate and a friction material. The metal backing plate provides structural support for the brake pad, ensuring proper integration with other components of the braking system. The friction material, situated on the surface of the metal backing plate, is the part that comes into contact with the disc, generating friction to slow down or stop the vehicle. These friction materials are typically composed of wear-resistant materials to ensure durability and braking performance.

Types of Brake Pads:
1
Organic Brake Pads
Made from natural materials like rubber, glass, and resins. They offer quiet operation and smooth braking but may wear out faster and produce more brake dust.
2
Semi-Metallic Brake Pads
Formulated with metal fibers and other materials, offering improved heat dissipation and durability compared to organic pads. They are suitable for a wide range of driving conditions but may produce more noise and brake dust.
3
Ceramic Brake Pads
Constructed with ceramic compounds, providing excellent heat resistance, durability, and low noise levels. They produce less brake dust and offer consistent braking performance, making them popular for everyday driving.
4
Carbon Fiber Brake Pads
Utilize carbon fibers for their high temperature tolerance and lightweight properties. They offer exceptional braking performance, especially at high speeds, and are commonly used in high-performance and racing vehicles.
How Do Brake Pads Work?
The working principle of vehicle brake pads.
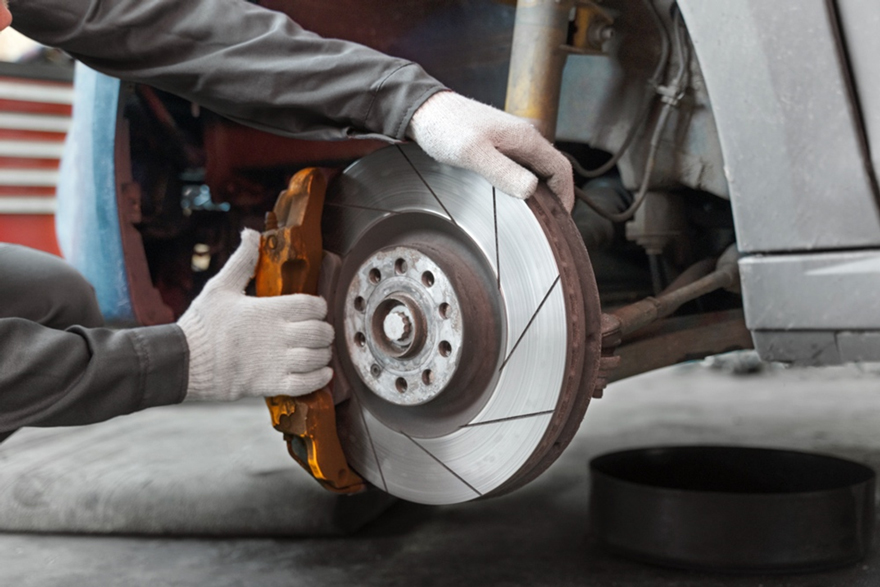

Brake pads function within vehicles based on the principle of friction. The main operational procedure is as follows:
- Application of force: When the driver presses the brake pedal, the hydraulic system transmits pressure to the brake caliper, or mechanical systems deliver force to the brake pads.
- Compression of brake pads: The brake caliper contains brake pads. When force is applied, the brake caliper compresses the brake pads onto the rotating disc.
- Generation of friction: The compressed brake pads come into contact with the surface of the disc, generating friction. This causes the disc's motion to decelerate, simultaneously converting kinetic energy into heat energy.
- Deceleration and stopping: After friction occurs, the motion of the wheels slows down, and the vehicle follows suit, ultimately stopping. This enables the driver to control the vehicle's speed and stop.
- Release of brakes: When the driver releases the brake pedal, hydraulic or mechanical systems release the brake pressure, allowing the brake pads to separate from the disc. This enables the wheels to resume free rotation, allowing the vehicle to continue moving forward.
Brake pads create friction against the surface of the disc, converting the vehicle's kinetic energy into heat energy to achieve deceleration or stopping. This plays a crucial role in the vehicle's braking system, ensuring the safety of the driver and passengers. More information
The working principle of bicycle disc brake pads.
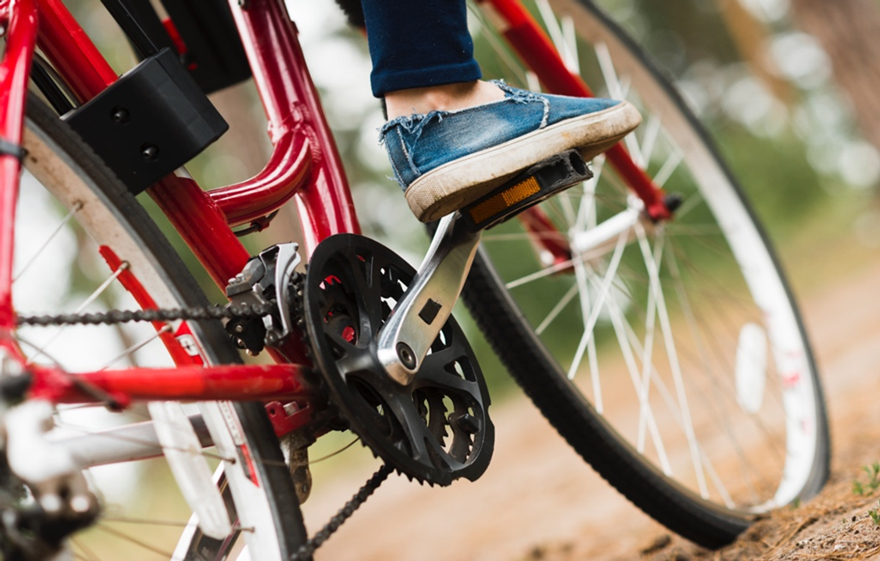

When the rider presses the brake lever, it pulls the brake cable, transmitting pressure to the brake caliper. This pressure compresses the brake pads inside the caliper against the wheel's rim or disc. The friction surface of the brake pads makes contact with the wheel's rim or disc, generating friction force.
This slows down the rotation of the wheel's rim or disc, converting the bicycle's kinetic energy into heat energy, thereby decelerating or stopping the bicycle. When the rider releases the brake lever, the brake caliper releases the brake pads, allowing them to separate from the wheel's rim or disc, and the bicycle resumes normal operation." More information
The working principle of brake pads for E-bike/E-motor.
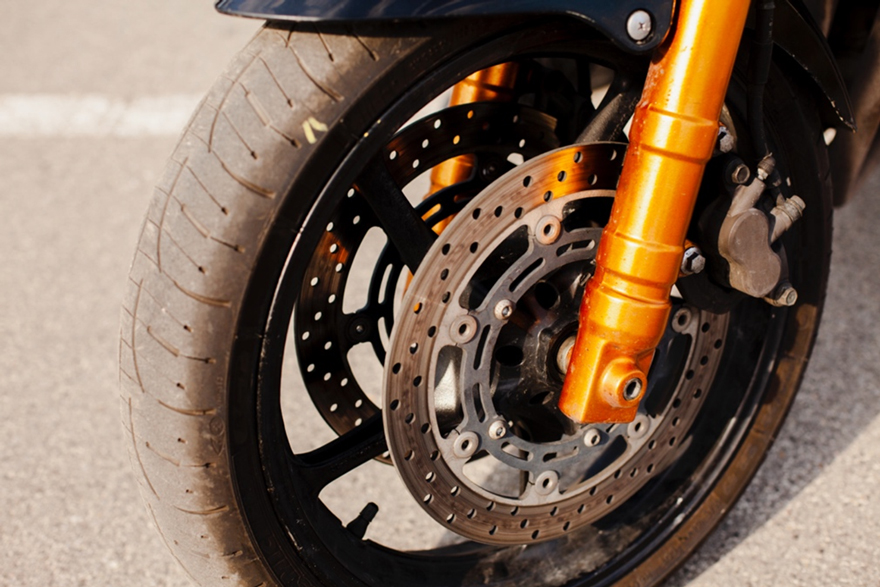

The operating principle of brake pads for E-bike/E-motor is similar to that of traditional cars or motorcycles, but with some specific features for electric vehicles. Here is the basic working principle:
- Brake System Type: E-bike/E-motor typically use a disc brake system, where the brake caliper is fixed to the frame and the disc is attached to the wheel.
- Operation: The rider activates the brake system by pulling the brake lever or pressing the brake pedal.
- Hydraulic or Mechanical System: The brake system can be hydraulic or mechanical, depending on the vehicle's design and model. Hydraulic brake systems use hydraulic pressure to transmit force, while mechanical brake systems use mechanical structures to transmit force.
- Brake Pads and Disc: When the brake lever or pedal is operated, hydraulic or mechanical force compresses the brake pads inside the brake caliper against the rotating disc, generating friction. This slows down or stops the rotation of the wheel, thereby decelerating or stopping the vehicle.
- Brake Release: When the brake lever or pedal is released, the brake caliper releases the brake pads, allowing the disc and wheel to rotate freely again, enabling the vehicle to continue moving.
The brake pads of E-bike/E- motor generate friction when they come into contact with the disc, converting the kinetic energy of the wheels into heat energy, achieving deceleration or stopping. This provides E-bike/E- motor with better braking performance and control. More information
The working principle of brake pads for industrial/agricultural machinery.
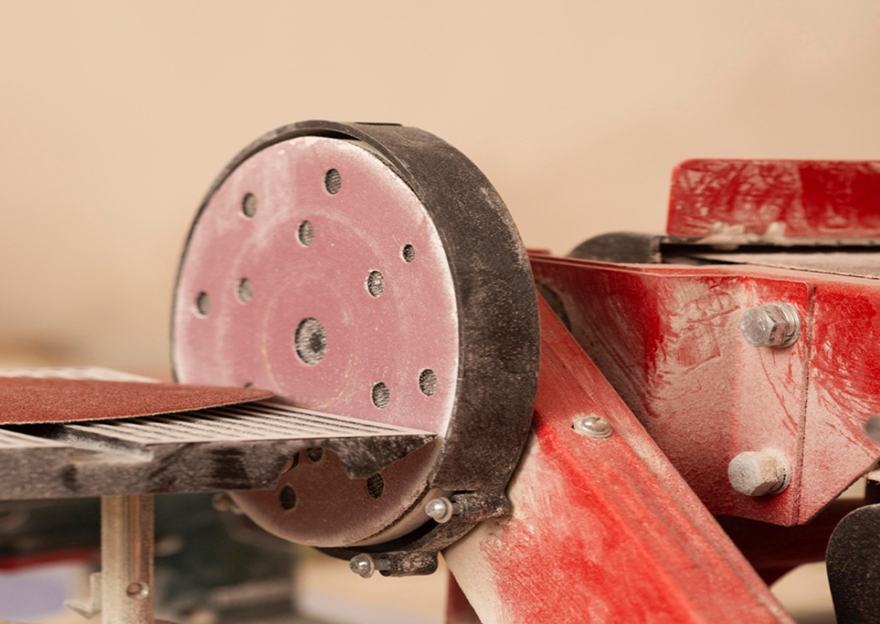

The working principle of brake pads for industrial/agricultural machinery is similar to that of other vehicle braking systems. When the operator applies the brakes, the brake system transfers pressure to the brake pads, causing them to make contact with mechanical components(such as discs), thereby slowing down or stopping the machinery's motion.
When the brakes are released, the pressure is released, and the brake pads separate from the mechanical components, allowing the machinery to resume normal operation. More information
Choosing the right brake pads is crucial for vehicle performance and safety. Different vehicles may require different types of brake pads to meet their performance and usage requirements. For instance, high-performance vehicles might necessitate brake pads with higher temperature tolerance and more robust braking capabilities, while daily-driven passenger cars might prioritize comfort and longevity.
The performance of brake pads is influenced by various factors, including the quality of the friction material, the compatibility of the friction material with the disc or drum, the design of the braking system, and operating conditions. Therefore, careful consideration should be given to factors such as vehicle type, usage, and environment when selecting and installing brake pads to ensure they deliver stable and reliable braking performance.
ADUI BRAKE offers brake pads & Custom Brake Pads to meet the specific needs of our clients.With 25 years of experience in custom production Brake Pads for a variety of material. If you need an experienced and skillful Custom Brake Pads supplier, please